Overview of accreditation
Aim and method of accreditation
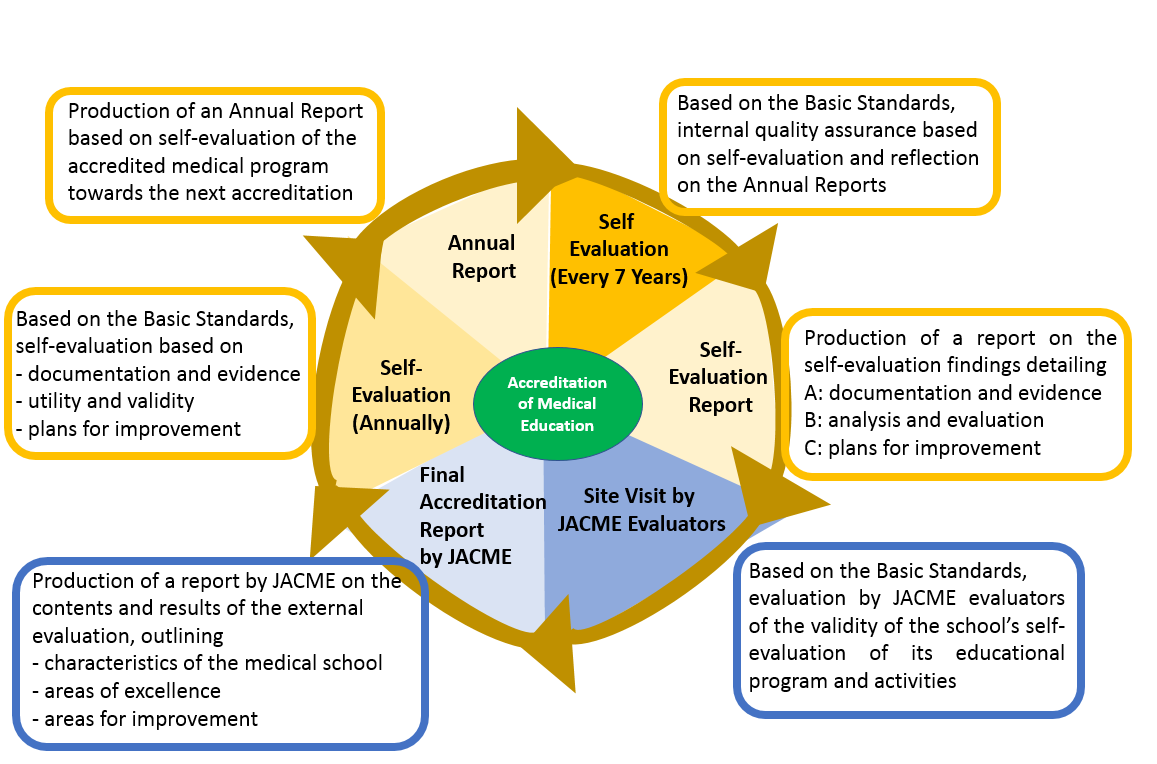
Accreditation of a medical school by the Japan Accreditation Council for Medical Education (JACME) is conducted through a self-evaluation and an external evaluation. First, the applying medical school prepares a self-evaluation report to identify areas of excellence in the school’s medical education program as well as areas for improvement and plans how to further enhance areas of excellence and amend areas that need improvement. During the subsequent external evaluation, the self-evaluation report written by the school’s faculty is objectively and fairly reviewed by a third-party team of JACME evaluators and the contents are confirmed through a site visit, at the end of which the evaluators make a judgement on whether each of the criteria has been met. The process of accreditation aims to stimulate the faculty of the medical school to reflect on their educational program, identify problem areas, and continuously improve the quality of the educational program.
JACME has established Japanese Specifications based on the Basic Medical Education WFME Global Standards for Quality Improvement, and accredits medical schools in Japan using these specifications. Every medical school that underwent accreditation by JACME must publish the self-evaluation report and the results of the evaluation by JACME on its website. Through this, every medical school contributes to the quality assurance of medical education and the development of medical doctors who are trusted and respected by society.
Process of accreditation
Evaluation by JACME does not simply result in a “pass”, “fail” or “pending” decision. The process of accreditation helps the faculty of the medical school reflect on their educational program through self-evaluation and through dialogue with the JACME evaluators.